THE RESEARCH IS IN:
FREQUENT INSULIN TITRATION WITH
d-Nav® TECHNOLOGY2 IMPROVES SAFETY & EFFICACY OF TREATMENT.
Studies demonstrate that adjusting a patient's insulin dose regularly is a good way to improve treatment safety and efficacy.

IN A MULTI-SITE RANDOMIZED CONTROL STUDY, d-Nav TECHNOLOGY2 IMPROVED A1C WITHOUT INCREASING THE RISK FOR HYPOGLYCEMIA.*
Studies show, by monitoring both high and low blood glucose levels, d-Nav drastically reduced the frequency and severity of hypoglycemia and improved A1C within three months.
CONTACT
Let us know if we can help.
* Bergenstal, R. M., Johnson, M., Passi, R., Bhargava, A., Young, N., Kruger,D. F., Bashan, E., Bisgaier, S. G., Isaman,D. J. M.,& Hodish, I.(2019). Automated insulin dosing guidance to optimise insulin management in patients with type 2 diabetes: a multicentre,randomised controlled trial. The Lancet, 393(10176), 1138–1148. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(19)30368-x
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
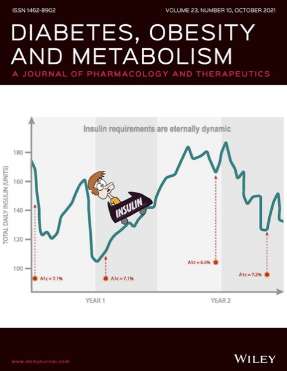
Insulin Requirements are Eternally Dynamic
Hodish I. Letter to The Editor: Insulin Requirements are Eternally Dynamic. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism. 2021 Oct;23(10):2409-2410. Accompanied with an artwork issue cover.
This front-page illustration that was commissioned by Diabetes, Obesity and metabolism, following an editorial, highlights the dynamic nature of insulin requirements on a day-to-day setting, and the need for frequent titration to maintain the efficacy and safety of the therapy.
https://dom-pubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/dom.14460
PEER-REVIEWED PAPERS

Automated Insulin Dosing Guidance to Optimize Insulin Management in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes; A Multi-Center Randomized-Controlled Trial
Bergenstal MR, Johnson M, Passi R, Bhargava A, Young N, Kruger FD, Bashan E, Bisgaier GS, Marriot JMI, Hodish I. Automated Insulin Dosing Guidance to Optimize Insulin Management in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes; A Multi-Center Randomized-Controlled Trial. Lancet. 2019 Mar 16;393(10176):1138-1148.
This pivotal NIH-funded, US-based, multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical study, was published in the LANCET in 2019. A diverse population of 181 patients with type 2 diabetes using insulin were recruited in 3 different states and followed for 6 months. The study established the clinical superiority of d-Nav automated insulin titration guidance with health care providers support compared to health care providers support alone. Despite improved glycemic control on d-Nav therapy, treatment safety was preserved. The article was followed by a favorable editorial and a New England Journal of Medicine, Journal Watch review.
https://www.thelancet.com/article/S0140-6736(19)30368-X/fulltext

Temporary Reductions in Insulin Requirements Are Associated with Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes
Harper R, Bashan E, Bisgaier SG, Willis M, Isaman DJM, Hodish I. Temporary Reductions in Insulin Requirements Are Associated with Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes. 2018 Dec;20(12):817-824.
This retrospective clinical study quantified the dynamics in insulin requirements over time in the context of treatment safety. It included data from 246 patients with type 2 diabetes who have used d-Nav for a period of almost 3 years. While maintaining an average HbA1c of about 7%-7.5%, with low hypoglycemic burden, about two third of patients experienced episodes of decrease in insulin requirements every about 15 months. The episodes lasted for 10 weeks in average, during which insulin needs decreased by about 40%. Almost of half of the hypoglycemic events occurred during these periods. Seasons of the year, gender, age, BMI, and HbA1c were not found to be predictors for the drops in insulin requirements. Interestingly, while using d-Nav, the safety of efficacy of premixed regimen in these patients were similar to basal-bolus regimen.

Insulin Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes – Are We There Yet? The d-Nav® Story
Hodish I. Insulin Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes – Are We There Yet? The d-Nav® Story. Clin Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018 Apr 10;4:8.
This review paraphrases the scientific merits and clinical outcomes of the d-Nav Insulin Management Service, in the context of the shortcoming of the standard-of-care in insulin management.
https://clindiabetesendo.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40842-018-0056-5

Journal of Health Economics and Outcomes Research
Schneider JE, Parikh A, Stojanovic I. Impact of a novel insulin management service on non-insulin pharmaceutical expenses. Journal of Health Economics and Outcomes Research 2018;6(1):53-62.
This prospective clinical study in 192 d-Nav users with insulin treated type 2 diabetes, examined the pharmacological cost saving potential of the d-Nav Insulin Management Service. Improved glycemia, allowed reconsideration of non-insulin anti-diabetes medications. Direct savings from medication elimination was estimated to be $1,736 per patient per year for all patients and $6172 for the target group who used expensive medications.

Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of d-Nav for People with Diabetes at High Risk of Neuropathic Foot Ulcers
Green W, Taylor M. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of d-Nav for People with Diabetes at High Risk of Neuropathic Foot Ulcers. Diabetes Therapy. 2016 Sep;7(3):511-25. PMID: 27402392.
This study modeled the cost-effectiveness of the d-Nav Insulin Management Program’s glycemic benefit in 122 patients with insulin treated type 2 diabetes at risk of developing neuropathic foot ulcers. It was oriented toward the British National Health Service (NHS) cost of care. d-Nav was cost-saving and produced more QALYs (Quality-Adjusted Life-Years) than the standard of care, with a total net monetary benefit value of £1459 per patient.

Dynamics in Insulin Requirements and Treatment Safety
Harper R, Donnelly R, Bi Y, Bashan R, Minhas R, Hodish I. Dynamics in Insulin Requirements and Treatment Safety. Journal of Diabetes Complications. 2016 Sep-Oct;30(7):1333-8.
This retrospective clinical study with 62 d-Nav users with insulin treated type 2 diabetes, was the first report quantifying the dynamics ins insulin requirements over time. It followed patients for more than 2 years, while average HbA1c was kept at about 7%-7.5% with low hypoglycemic burden. About two third of patients experienced unpredictable events of considerable decrease in insulin requirements that lasted for months. These periods could put patients at risk for excessive hypoglycemia unless accompanied with frequent insulin titrations.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1056872716301702?via%3Dihub

A Novel Approach to Optimize Glycemic Control in Insulin Users
Bashan E, Harper R, Bi Y, Hodish I. A Novel Approach to Optimize Glycemic Control in Insulin Users. BMJ Case Rep. 2015 Jul 31.
This collection of case reports, describes the logic behind the d-Nav technology by providing examples from users.

Diabetes Insulin Guidance System: a real-world evaluation of new technology (d-Nav) to achieve glycaemic control in insulin-treated type 2 diabetes
Donnelly R, Carr S, Harper R. Diabetes Insulin Guidance System: a real-world evaluation of new technology (d-Nav) to achieve glycaemic control in insulin-treated type 2 diabetes. Practical Diabetes. 2015 32(7):247-252. Discusses Hodish’s innovations.
This service evaluation that was done at the Ulster Hospital, Belfast, UK, followed 122 patients using d-Nav for insulin treated type 2 diabetes for a year. HbA1c has improved dramatically and maintained stable, with low hypoglycemic load.

Can a Tool that Automates Insulin Titration be a Key to Diabetes Management?
Bergenstal RM, Bashan E, McShane M, Johnson M, Hodish I. Can a Tool that Automates Insulin Titration be a Key to Diabetes Management? 2012 Diabetes Technol Ther. 2012 Aug;14(8):675-82.
This NIH-funded single group prospective feasibility-clinical study with 46 patients with type 1 and insulin treated type 2 diabetes, demonstrated the efficacy and safety of the d-Nav software’s insulin doses titrations that were approved by an expert study team.

Frequent Insulin Dosage Adjustments Based on Glucose Readings Alone are Sufficient for a Safe and Effective Therapy
Bashan E, Hodish I. Frequent Insulin Dosage Adjustments Based on Glucose Readings Alone are Sufficient for a Safe and Effective Therapy. J Diabetes Complications. 2012 May-Jun;26(3):230-6.
This proof-of-concept prospective clinical trial, in 14 patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, showed that glucose readings are sufficient to adjust insulin therapy in a safe and effective manner, when adjustments are made on a weekly basis.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1056872712000529?via%3Dihub

Are Glucose Readings Sufficient to Adjust Insulin Dosage?
Bashan E, Herman WH, Hodish I. Are Glucose Readings Sufficient to Adjust Insulin Dosage? Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011 Jan;13(1):85-92. PMID: 21175277.
This proof-of-concept retrospective clinical trial investigated data from 26 elderly patients with type 2 diabetes treated with basal-bolus insulin therapy for a year. Insulin doses were titrated by an expert study team every 1-4 weeks. The algorithm used by d-Nav, was used to give recommendations for insulin doses adjustments based only on glucose levels. The d-Nav software recommendations for dosage adjustments were clinically equivalent to the original study team’s recommendations in the overwhelming majority of the cases, without unsafe discrepancies.
BECOME A d-NAV PARTNER
Realize functional and financial benefits for your practice.
REFER A PATIENT
Put those who depend on you on a better track.
